Nutritional Composition of Pineapple

Nutrl pineapple nutrition facts – Pineapple, a tropical fruit renowned for its sweet and tangy flavor, offers a surprisingly diverse nutritional profile. Beyond its delightful taste, this fruit contributes significantly to a balanced diet, providing a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. A deeper examination of its macronutrient and micronutrient composition reveals its considerable nutritional value.
Nutrl pineapple, a popular choice for its refreshing taste, boasts a decent vitamin C profile. However, for those seeking a different nutritional powerhouse, exploring grains like bajra offers a unique set of benefits. Check out the comprehensive nutrition facts of bajra to compare its fiber and mineral content with Nutrl pineapple’s. Ultimately, both contribute to a balanced diet, each offering distinct nutritional advantages.
Macronutrient Breakdown of Pineapple, Nutrl pineapple nutrition facts
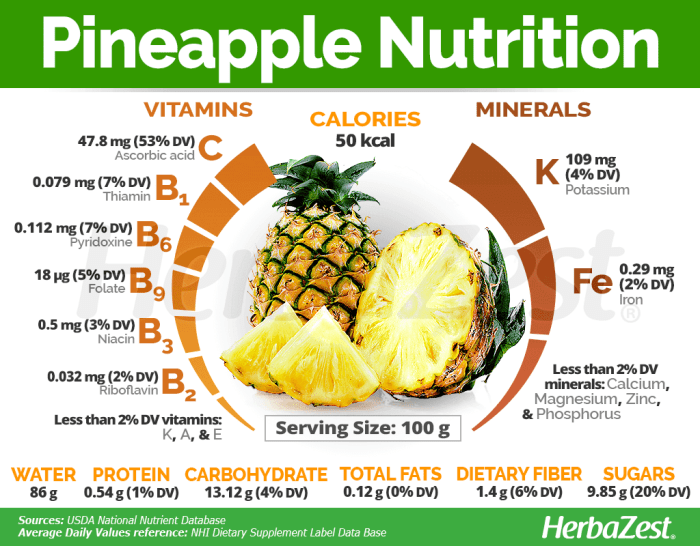
The macronutrient content of pineapple, like many fruits, is predominantly comprised of carbohydrates, with a smaller contribution from protein and negligible amounts of fat. The following table provides a representative breakdown of the macronutrients in a single cup (approximately 165g) of fresh pineapple chunks:
| Nutrient | Amount per serving | % Daily Value | Unit of Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 16.3g | 5% | grams |
| Sugars | 13.2g | – | grams |
| Fiber | 2.3g | 9% | grams |
| Protein | 0.9g | 2% | grams |
| Fat | 0.2g | 0% | grams |
*Note: Daily Value percentages are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Individual needs may vary.*
Micronutrient Profile of Pineapple
Pineapple’s nutritional richness extends beyond macronutrients to encompass a variety of essential micronutrients. These contribute to various bodily functions and overall health. A notable concentration of vitamins and minerals further enhances its nutritional value.
The following list highlights some key micronutrients found in pineapple:
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant crucial for immune function and collagen synthesis.
- Manganese: Essential for bone health, metabolism, and wound healing.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Plays a vital role in brain development and red blood cell formation.
- Thiamin (Vitamin B1): Supports carbohydrate metabolism and nerve function.
- Folate (Vitamin B9): Important for cell growth and development, especially during pregnancy.
- Copper: Contributes to iron absorption and energy production.
- Potassium: An essential electrolyte that helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
Dietary Fiber in Pineapple and Digestive Health
Pineapple contains a significant amount of dietary fiber, primarily in the form of insoluble fiber. This type of fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. The fiber content also contributes to a feeling of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management. Furthermore, the fiber in pineapple supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, contributing to a healthy gut microbiome.
Adequate fiber intake is crucial for optimal digestive health, and pineapple offers a delicious and natural way to increase fiber consumption.
Health Benefits Associated with Pineapple Consumption: Nutrl Pineapple Nutrition Facts
The vibrant, tropical sweetness of pineapple belies a wealth of nutritional benefits extending far beyond its delicious taste. This fruit, a powerhouse of vitamins, minerals, and unique enzymes, offers a compelling array of advantages for overall health and well-being, impacting everything from immune function to digestive health. Its multifaceted properties make it a worthy addition to a balanced diet.Pineapple’s contribution to a robust immune system is significant, largely due to its vitamin C content.
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals and bolstering the body’s natural defenses against infection. Furthermore, manganese, another key nutrient found in pineapple, plays a vital role in immune function by supporting the activity of various enzymes involved in immune response. The fruit also provides modest amounts of other immune-supporting vitamins, such as vitamin B6 and folate.
The Anti-inflammatory Role of Bromelain
Bromelain, a complex mixture of protein-digesting enzymes found primarily in the stem and juice of pineapple, is responsible for many of the fruit’s purported health benefits. Extensive research suggests that bromelain possesses notable anti-inflammatory properties. These properties are attributed to bromelain’s ability to inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, thereby reducing inflammation in the body.
While further research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms and clinical applications, studies have shown promising results in managing inflammation associated with various conditions, including arthritis and sinusitis. The anti-inflammatory effects of bromelain are not solely reliant on its enzymatic activity; it also demonstrates anti-edema and fibrinolytic effects, contributing to its overall impact on reducing inflammation.
Pineapple and Digestive Health
Pineapple’s contribution to digestive health is largely attributed to the presence of bromelain and its fiber content. Bromelain’s proteolytic activity aids in the breakdown of proteins, facilitating digestion and potentially reducing symptoms of indigestion. The dietary fiber present in pineapple contributes to healthy bowel movements, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. The combination of bromelain’s enzymatic action and the fiber content makes pineapple a valuable ally in supporting optimal gut health.
Furthermore, the prebiotic potential of pineapple, although not extensively researched, suggests a role in nourishing beneficial gut bacteria, further enhancing digestive function.
Question Bank
Is canned pineapple as nutritious as fresh pineapple?
While canned pineapple retains some nutrients, fresh pineapple generally boasts higher levels of vitamins and fiber due to minimal processing.
Can I eat pineapple every day?
Moderate consumption is generally safe, but excessive intake might cause digestive upset in some individuals due to its acidity. Listen to your body and adjust your intake accordingly.
Does pineapple interact with blood thinners?
Bromelain, found in pineapple, may interact with blood thinners. Consult your doctor if you are on blood thinners before significantly increasing your pineapple consumption.
Is pineapple good for people with diabetes?
Pineapple contains natural sugars, so those with diabetes should consume it in moderation and monitor their blood sugar levels.

