Black-Eyed Peas in Different Diets
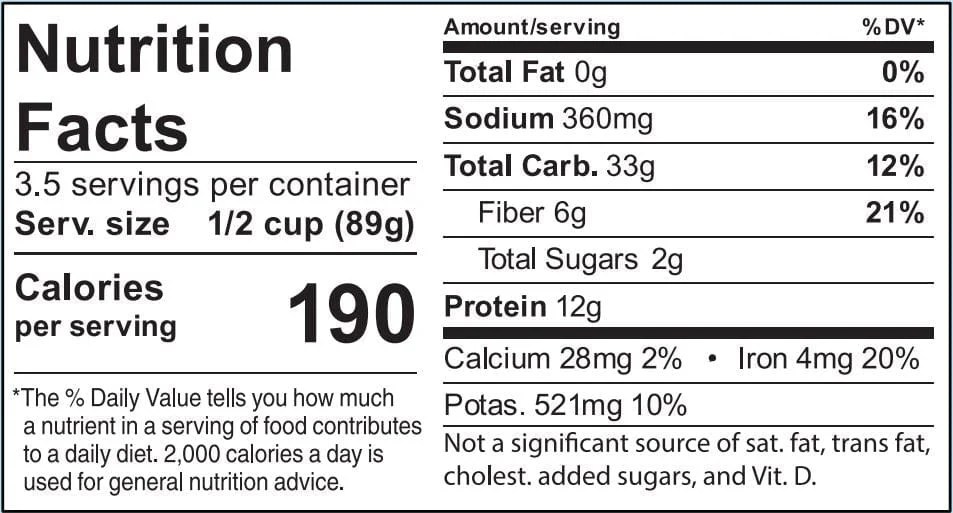
Nutrition facts black eyed peas – Black-eyed peas are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a compelling addition to various dietary plans. Their versatility and impressive nutrient profile make them a valuable asset for vegetarians, vegans, those watching their weight, and anyone seeking a healthy and delicious boost to their meals. Let’s explore how these humble legumes can enhance your diet.
Black-Eyed Peas in Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
For vegetarians and vegans, black-eyed peas are an excellent source of plant-based protein, crucial for building and repairing tissues. A single cup of cooked black-eyed peas provides approximately 15 grams of protein, contributing significantly to the daily protein needs of individuals following plant-based diets. This protein, combined with their fiber content, promotes satiety, helping manage hunger and preventing overeating.
Yo, check the nutritional facts on black eyed peas, proper healthy vibes, innit? But if you’re craving something sweet, you might wanna peep the mini twix nutrition facts – then straight back to those black eyed peas for a bit of balance, yeah? Keeps the energy levels right and the waistline looking decent.
Incorporating black-eyed peas into meals like stews, salads, or as a side dish provides a satisfying and nutritious protein source without relying on animal products.
Nutritional Comparison of Black-Eyed Peas with Other Legumes
Black-eyed peas compare favorably to other popular legumes in terms of nutritional value. While the exact nutritional composition can vary slightly based on growing conditions and preparation methods, the following table provides a general comparison:
| Nutrient | Black-Eyed Peas (1 cup cooked) | Lentils (1 cup cooked) | Chickpeas (1 cup cooked) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (grams) | ~15 | ~18 | ~15 |
| Fiber (grams) | ~8 | ~16 | ~12 |
| Iron (mg) | ~3 | ~6 | ~4 |
| Folate (mcg) | ~170 | ~180 | ~150 |
| Calories | ~220 | ~230 | ~270 |
Note: These values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific variety and preparation method.
Black-Eyed Peas in Weight-Management Diets
Black-eyed peas can be a valuable component of weight-management strategies. Their high fiber content contributes to increased satiety, meaning you feel fuller for longer after eating them, reducing overall calorie intake. Furthermore, their relatively low calorie density (compared to some other protein sources) allows for larger portion sizes while maintaining a reasonable calorie count. Including black-eyed peas in meals can help manage hunger pangs and cravings, supporting weight loss or maintenance goals.
For example, swapping a high-calorie side dish for a serving of black-eyed peas can significantly reduce the overall calorie intake of a meal without compromising on taste or nutritional value. Studies have shown that diets rich in fiber, like those including black-eyed peas, are associated with improved weight management outcomes.
Health Benefits Associated with Black-Eyed Pea Consumption: Nutrition Facts Black Eyed Peas

Unlock the nutritional powerhouse within black-eyed peas and discover how these humble legumes can significantly contribute to your overall well-being. Packed with essential nutrients and fiber, black-eyed peas offer a multitude of health benefits, impacting everything from your heart health to your gut microbiome.
Black-Eyed Peas and Heart Health
Black-eyed peas are a nutritional champion for heart health, boasting a profile rich in fiber, folate, and magnesium – all crucial for maintaining cardiovascular wellness. The high fiber content helps lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, contributing to a healthier cholesterol profile. Furthermore, the potassium in black-eyed peas helps counterbalance the effects of sodium, thereby supporting healthy blood pressure management.
Regular consumption can contribute to a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke. For example, studies have shown a correlation between diets rich in legumes, like black-eyed peas, and a lower incidence of cardiovascular events.
Black-Eyed Peas and Blood Sugar Regulation
The slow-digesting carbohydrates and high fiber content in black-eyed peas make them an excellent choice for individuals managing blood sugar levels, including those with diabetes. Unlike refined carbohydrates that cause rapid spikes in blood glucose, black-eyed peas provide a sustained release of energy, preventing drastic fluctuations. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
The fiber also promotes satiety, aiding in weight management, another important factor in diabetes control. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition demonstrated the positive impact of legume consumption on glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Black-Eyed Peas and Gut Health, Nutrition facts black eyed peas
Black-eyed peas are a fantastic source of dietary fiber, both soluble and insoluble. This fiber is crucial for fostering a thriving gut microbiome. Soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial bacteria in your gut, while insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved immunity, better digestion, and reduced inflammation throughout the body.
The abundance of resistant starch in black-eyed peas further contributes to the nourishment of beneficial gut bacteria. Imagine the positive impact on your digestive system and overall health with the regular inclusion of this nutrient-rich legume in your diet.
FAQ Compilation
Are black-eyed peas gluten-free?
Yes, black-eyed peas are naturally gluten-free.
Can I eat black-eyed peas every day?
While black-eyed peas are nutritious, a balanced diet is key. Daily consumption is fine as part of a varied eating plan, but don’t rely on them as your sole source of nutrients.
How do I store leftover black-eyed peas?
Store cooked black-eyed peas in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days. Freezing is also an option for longer storage.
Are black-eyed peas good for weight loss?
Their high fiber content promotes satiety, which can aid in weight management. However, portion control is crucial, as they still contain calories.

