Nutritional Composition of 1 Cup of Cottage Cheese
1 cup of cottage cheese nutrition facts – Cottage cheese offers a versatile and nutritious addition to a balanced diet. Its nutritional profile varies depending on the fat content, but generally provides a good source of protein and calcium. Understanding the macronutrient and micronutrient breakdown allows for informed dietary choices.
Macronutrient Composition of 1 Cup of Cottage Cheese
A typical 1-cup serving of low-fat cottage cheese (around 225g) contains approximately 28 grams of protein, 5 grams of fat, and 6 grams of carbohydrates. The percentages of daily value will vary based on individual daily caloric needs, but as a general guideline, this serving provides a significant portion of the recommended daily protein intake. The fat content contributes to satiety, and the carbohydrates provide a small amount of energy.
Full-fat varieties will have a higher fat content, while reduced-fat options will contain less fat but often slightly more carbohydrates. Precise values can fluctuate slightly depending on the brand and manufacturing process.
One cup of cottage cheese boasts a surprisingly high protein content, perfect for a healthy snack or meal prep. However, if you’re craving something sweeter, comparing this to the sugar content in a starbucks green tea frappuccino nutrition facts highlights the significant difference in caloric density. Ultimately, choosing cottage cheese often provides a more balanced nutritional profile for weight management and overall health.
Micronutrient Content of 1 Cup of Cottage Cheese, 1 cup of cottage cheese nutrition facts
Cottage cheese is a source of several essential vitamins and minerals. The following table provides an approximate breakdown of micronutrients in a 1-cup serving of low-fat cottage cheese. Note that values can vary slightly depending on the brand and processing methods.
| Nutrient | Quantity (Approximate) | Nutrient | Quantity (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 20% Daily Value | Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 20% Daily Value |
| Phosphorus | 15% Daily Value | Vitamin B12 | 15% Daily Value |
| Selenium | 10% Daily Value | Vitamin A | 5% Daily Value |
| Potassium | 5% Daily Value | Zinc | 5% Daily Value |
Nutritional Differences Between Cottage Cheese Varieties
The nutritional content of cottage cheese significantly differs based on its fat content. Here’s a comparison of low-fat, reduced-fat, and full-fat varieties:
- Low-fat cottage cheese: Lower in total fat and calories, making it a suitable option for those watching their fat intake. Protein content remains relatively high.
- Reduced-fat cottage cheese: Contains a moderate amount of fat, offering a balance between flavor and reduced calorie intake compared to full-fat options. Protein content is generally similar to low-fat.
- Full-fat cottage cheese: Higher in total fat and calories, providing a richer flavor and creamier texture. Protein content is comparable to other varieties, but the increased fat content should be considered in the context of individual dietary goals.
Health Benefits Associated with Cottage Cheese Consumption

Cottage cheese offers a surprising array of health benefits stemming from its unique nutritional profile. Its high protein and calcium content, combined with a relatively low fat and carbohydrate profile (depending on the variety), makes it a versatile and valuable addition to a balanced diet. The benefits extend beyond simple nutrition, impacting muscle health, weight management, and overall well-being.Cottage cheese’s role in muscle building and repair is significant.
Muscle Building and Repair
The high protein content in cottage cheese is crucial for muscle growth and repair. Protein provides the essential amino acids needed to build and maintain muscle tissue. After a workout, consuming cottage cheese helps replenish these amino acids, supporting muscle recovery and growth. This is particularly beneficial for individuals engaged in regular strength training or other forms of physical activity.
The casein protein found in cottage cheese is a slow-digesting protein, providing a sustained release of amino acids into the bloodstream, which further supports muscle protein synthesis throughout the night. This makes it an ideal snack before bed for those aiming to maximize muscle growth.
Impact on Satiety and Weight Management
Cottage cheese’s ability to promote satiety, or feelings of fullness, is a key factor in its contribution to weight management strategies. The combination of protein and calcium helps regulate appetite hormones, reducing hunger pangs and cravings. This can lead to reduced overall calorie intake, contributing to weight loss or maintenance. A study published in theInternational Journal of Obesity* demonstrated that individuals consuming a high-protein breakfast, including cottage cheese, experienced greater feelings of fullness and consumed fewer calories throughout the day compared to those consuming a lower-protein breakfast.
This prolonged satiety effect can be particularly helpful for individuals aiming to manage their weight effectively.
Contribution to Bone Health and Overall Well-being
The significant calcium content in cottage cheese is vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Calcium is a key structural component of bone tissue, and adequate intake is crucial for preventing osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions. Cottage cheese also provides a good source of phosphorus, another essential mineral for bone health. Moreover, the protein in cottage cheese supports overall well-being by contributing to healthy muscle mass, immune function, and various metabolic processes.
A diet rich in calcium and protein, such as one that includes regular cottage cheese consumption, can contribute significantly to overall health and reduce the risk of age-related bone loss and fragility.
Comparison with Other Dairy Products

Cottage cheese, often overlooked in the dairy aisle, holds a unique nutritional profile compared to its more popular counterparts like yogurt, milk, and cheese. Understanding these differences is key to making informed choices about which dairy product best suits individual dietary needs and preferences. This comparison will examine the macronutrient content and potential health implications of each option.
While all dairy products offer varying degrees of protein, calcium, and other essential nutrients, their composition significantly differs. These differences impact their suitability for various dietary goals, such as weight management, muscle building, or simply maintaining overall health. For instance, the high protein content of cottage cheese makes it a popular choice for those focusing on muscle growth, while the probiotic content of yogurt supports gut health.
Macronutrient Comparison of Dairy Products
The following table provides a general comparison of the macronutrient content per serving (approximately one cup or equivalent) of cottage cheese, yogurt, milk, and cheese. Note that the specific values can vary depending on the type of dairy product (e.g., fat content, flavorings). These figures represent averages based on common commercially available products.
| Dairy Product | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese (low-fat) | 25-30 | 5-10 | 5-8 |
| Yogurt (plain, non-fat) | 15-20 | 0-2 | 15-20 |
| Milk (whole) | 8-9 | 8-10 | 12-13 |
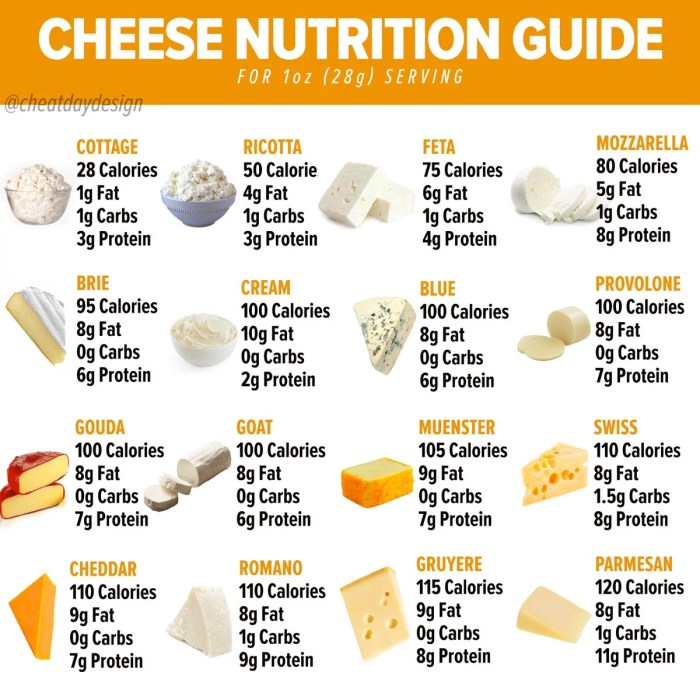
| Cheddar Cheese (1 ounce) | 7 | 9 | 1 |
It’s important to note that this table provides a simplified comparison. The actual nutritional content can vary greatly depending on factors such as the fat content of the dairy product, added sugars, and specific ingredients. For example, full-fat cottage cheese will have a significantly higher fat content than low-fat varieties, and flavored yogurts often contain added sugars that increase carbohydrate content.
Health Implications and Advantages/Disadvantages
The differences in macronutrient composition translate to different health implications. High-protein options like cottage cheese can promote satiety and support muscle growth, while low-fat options can be beneficial for weight management. Yogurt’s probiotic content contributes to gut health, and milk provides essential calcium for bone health. Cheese, while a good source of calcium and protein, should be consumed in moderation due to its higher fat and sodium content.
The ideal choice depends on individual dietary needs and health goals.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1 Cup Of Cottage Cheese Nutrition Facts
What are the potential downsides or allergies related to cottage cheese consumption?
Some individuals may experience lactose intolerance symptoms. Others may have allergies to dairy proteins. Those with sodium sensitivities should check the sodium content of different brands.
Can cottage cheese be incorporated into desserts?
Absolutely! Cottage cheese can be used in cheesecakes, muffins, and even as a creamy base for certain desserts, offering a healthier twist.
How does the protein in cottage cheese compare to other protein sources?
Cottage cheese provides a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. While its protein content is high compared to many other dairy products, it’s important to consider the overall protein needs based on individual activity levels and goals.

